- Docs Home
- About TiDB
- Quick Start
- Develop
- Overview
- Quick Start
- Build a TiDB Cluster in TiDB Cloud (Developer Tier)
- CRUD SQL in TiDB
- Build a Simple CRUD App with TiDB
- Example Applications
- Connect to TiDB
- Design Database Schema
- Write Data
- Read Data
- Transaction
- Optimize
- Troubleshoot
- Reference
- Cloud Native Development Environment
- Third-party Support
- Deploy
- Software and Hardware Requirements
- Environment Configuration Checklist
- Plan Cluster Topology
- Install and Start
- Verify Cluster Status
- Test Cluster Performance
- Migrate
- Overview
- Migration Tools
- Migration Scenarios
- Migrate from Aurora
- Migrate MySQL of Small Datasets
- Migrate MySQL of Large Datasets
- Migrate and Merge MySQL Shards of Small Datasets
- Migrate and Merge MySQL Shards of Large Datasets
- Migrate from CSV Files
- Migrate from SQL Files
- Migrate from One TiDB Cluster to Another TiDB Cluster
- Migrate from TiDB to MySQL-compatible Databases
- Advanced Migration
- Integrate
- Overview
- Integration Scenarios
- Maintain
- Monitor and Alert
- Troubleshoot
- TiDB Troubleshooting Map
- Identify Slow Queries
- Analyze Slow Queries
- SQL Diagnostics
- Identify Expensive Queries Using Top SQL
- Identify Expensive Queries Using Logs
- Statement Summary Tables
- Troubleshoot Hotspot Issues
- Troubleshoot Increased Read and Write Latency
- Save and Restore the On-Site Information of a Cluster
- Troubleshoot Cluster Setup
- Troubleshoot High Disk I/O Usage
- Troubleshoot Lock Conflicts
- Troubleshoot TiFlash
- Troubleshoot Write Conflicts in Optimistic Transactions
- Troubleshoot Inconsistency Between Data and Indexes
- Performance Tuning
- Tuning Guide
- Configuration Tuning
- System Tuning
- Software Tuning
- SQL Tuning
- Overview
- Understanding the Query Execution Plan
- SQL Optimization Process
- Overview
- Logic Optimization
- Physical Optimization
- Prepare Execution Plan Cache
- Control Execution Plans
- Tutorials
- TiDB Tools
- Overview
- Use Cases
- Download
- TiUP
- Documentation Map
- Overview
- Terminology and Concepts
- Manage TiUP Components
- FAQ
- Troubleshooting Guide
- Command Reference
- Overview
- TiUP Commands
- TiUP Cluster Commands
- Overview
- tiup cluster audit
- tiup cluster check
- tiup cluster clean
- tiup cluster deploy
- tiup cluster destroy
- tiup cluster disable
- tiup cluster display
- tiup cluster edit-config
- tiup cluster enable
- tiup cluster help
- tiup cluster import
- tiup cluster list
- tiup cluster patch
- tiup cluster prune
- tiup cluster reload
- tiup cluster rename
- tiup cluster replay
- tiup cluster restart
- tiup cluster scale-in
- tiup cluster scale-out
- tiup cluster start
- tiup cluster stop
- tiup cluster template
- tiup cluster upgrade
- TiUP DM Commands
- Overview
- tiup dm audit
- tiup dm deploy
- tiup dm destroy
- tiup dm disable
- tiup dm display
- tiup dm edit-config
- tiup dm enable
- tiup dm help
- tiup dm import
- tiup dm list
- tiup dm patch
- tiup dm prune
- tiup dm reload
- tiup dm replay
- tiup dm restart
- tiup dm scale-in
- tiup dm scale-out
- tiup dm start
- tiup dm stop
- tiup dm template
- tiup dm upgrade
- TiDB Cluster Topology Reference
- DM Cluster Topology Reference
- Mirror Reference Guide
- TiUP Components
- PingCAP Clinic Diagnostic Service
- TiDB Operator
- Dumpling
- TiDB Lightning
- TiDB Data Migration
- About TiDB Data Migration
- Architecture
- Quick Start
- Deploy a DM cluster
- Tutorials
- Advanced Tutorials
- Maintain
- Cluster Upgrade
- Tools
- Performance Tuning
- Manage Data Sources
- Manage Tasks
- Export and Import Data Sources and Task Configurations of Clusters
- Handle Alerts
- Daily Check
- Reference
- Architecture
- Command Line
- Configuration Files
- OpenAPI
- Compatibility Catalog
- Secure
- Monitoring and Alerts
- Error Codes
- Glossary
- Example
- Troubleshoot
- Release Notes
- Backup & Restore (BR)
- Point-in-Time Recovery
- TiDB Binlog
- TiCDC
- Dumpling
- sync-diff-inspector
- TiSpark
- Reference
- Cluster Architecture
- Key Monitoring Metrics
- Secure
- Privileges
- SQL
- SQL Language Structure and Syntax
- SQL Statements
ADD COLUMNADD INDEXADMINADMIN CANCEL DDLADMIN CHECKSUM TABLEADMIN CHECK [TABLE|INDEX]ADMIN SHOW DDL [JOBS|QUERIES]ADMIN SHOW TELEMETRYALTER DATABASEALTER INDEXALTER INSTANCEALTER PLACEMENT POLICYALTER TABLEALTER TABLE COMPACTALTER TABLE SET TIFLASH MODEALTER USERANALYZE TABLEBACKUPBATCHBEGINCHANGE COLUMNCOMMITCHANGE DRAINERCHANGE PUMPCREATE [GLOBAL|SESSION] BINDINGCREATE DATABASECREATE INDEXCREATE PLACEMENT POLICYCREATE ROLECREATE SEQUENCECREATE TABLE LIKECREATE TABLECREATE USERCREATE VIEWDEALLOCATEDELETEDESCDESCRIBEDODROP [GLOBAL|SESSION] BINDINGDROP COLUMNDROP DATABASEDROP INDEXDROP PLACEMENT POLICYDROP ROLEDROP SEQUENCEDROP STATSDROP TABLEDROP USERDROP VIEWEXECUTEEXPLAIN ANALYZEEXPLAINFLASHBACK TABLEFLUSH PRIVILEGESFLUSH STATUSFLUSH TABLESGRANT <privileges>GRANT <role>INSERTKILL [TIDB]LOAD DATALOAD STATSMODIFY COLUMNPREPARERECOVER TABLERENAME INDEXRENAME TABLEREPLACERESTOREREVOKE <privileges>REVOKE <role>ROLLBACKSAVEPOINTSELECTSET DEFAULT ROLESET [NAMES|CHARACTER SET]SET PASSWORDSET ROLESET TRANSACTIONSET [GLOBAL|SESSION] <variable>SHOW ANALYZE STATUSSHOW [BACKUPS|RESTORES]SHOW [GLOBAL|SESSION] BINDINGSSHOW BUILTINSSHOW CHARACTER SETSHOW COLLATIONSHOW [FULL] COLUMNS FROMSHOW CONFIGSHOW CREATE PLACEMENT POLICYSHOW CREATE SEQUENCESHOW CREATE TABLESHOW CREATE USERSHOW DATABASESSHOW DRAINER STATUSSHOW ENGINESSHOW ERRORSSHOW [FULL] FIELDS FROMSHOW GRANTSSHOW INDEX [FROM|IN]SHOW INDEXES [FROM|IN]SHOW KEYS [FROM|IN]SHOW MASTER STATUSSHOW PLACEMENTSHOW PLACEMENT FORSHOW PLACEMENT LABELSSHOW PLUGINSSHOW PRIVILEGESSHOW [FULL] PROCESSSLISTSHOW PROFILESSHOW PUMP STATUSSHOW SCHEMASSHOW STATS_HEALTHYSHOW STATS_HISTOGRAMSSHOW STATS_METASHOW STATUSSHOW TABLE NEXT_ROW_IDSHOW TABLE REGIONSSHOW TABLE STATUSSHOW [FULL] TABLESSHOW [GLOBAL|SESSION] VARIABLESSHOW WARNINGSSHUTDOWNSPLIT REGIONSTART TRANSACTIONTABLETRACETRUNCATEUPDATEUSEWITH
- Data Types
- Functions and Operators
- Overview
- Type Conversion in Expression Evaluation
- Operators
- Control Flow Functions
- String Functions
- Numeric Functions and Operators
- Date and Time Functions
- Bit Functions and Operators
- Cast Functions and Operators
- Encryption and Compression Functions
- Locking Functions
- Information Functions
- JSON Functions
- Aggregate (GROUP BY) Functions
- Window Functions
- Miscellaneous Functions
- Precision Math
- Set Operations
- List of Expressions for Pushdown
- TiDB Specific Functions
- Clustered Indexes
- Constraints
- Generated Columns
- SQL Mode
- Table Attributes
- Transactions
- Garbage Collection (GC)
- Views
- Partitioning
- Temporary Tables
- Cached Tables
- Character Set and Collation
- Placement Rules in SQL
- System Tables
mysql- INFORMATION_SCHEMA
- Overview
ANALYZE_STATUSCLIENT_ERRORS_SUMMARY_BY_HOSTCLIENT_ERRORS_SUMMARY_BY_USERCLIENT_ERRORS_SUMMARY_GLOBALCHARACTER_SETSCLUSTER_CONFIGCLUSTER_HARDWARECLUSTER_INFOCLUSTER_LOADCLUSTER_LOGCLUSTER_SYSTEMINFOCOLLATIONSCOLLATION_CHARACTER_SET_APPLICABILITYCOLUMNSDATA_LOCK_WAITSDDL_JOBSDEADLOCKSENGINESINSPECTION_RESULTINSPECTION_RULESINSPECTION_SUMMARYKEY_COLUMN_USAGEMETRICS_SUMMARYMETRICS_TABLESPARTITIONSPLACEMENT_POLICIESPROCESSLISTREFERENTIAL_CONSTRAINTSSCHEMATASEQUENCESSESSION_VARIABLESSLOW_QUERYSTATISTICSTABLESTABLE_CONSTRAINTSTABLE_STORAGE_STATSTIDB_HOT_REGIONSTIDB_HOT_REGIONS_HISTORYTIDB_INDEXESTIDB_SERVERS_INFOTIDB_TRXTIFLASH_REPLICATIKV_REGION_PEERSTIKV_REGION_STATUSTIKV_STORE_STATUSUSER_PRIVILEGESVARIABLES_INFOVIEWS
METRICS_SCHEMA
- UI
- TiDB Dashboard
- Overview
- Maintain
- Access
- Overview Page
- Cluster Info Page
- Top SQL Page
- Key Visualizer Page
- Metrics Relation Graph
- SQL Statements Analysis
- Slow Queries Page
- Cluster Diagnostics
- Monitoring Page
- Search Logs Page
- Instance Profiling
- Session Management and Configuration
- FAQ
- CLI
- Command Line Flags
- Configuration File Parameters
- System Variables
- Storage Engines
- Telemetry
- Errors Codes
- Table Filter
- Schedule Replicas by Topology Labels
- FAQs
- Release Notes
- All Releases
- Release Timeline
- TiDB Versioning
- TiDB Installation Packages
- v6.2
- v6.1
- v6.0
- v5.4
- v5.3
- v5.2
- v5.1
- v5.0
- v4.0
- v3.1
- v3.0
- v2.1
- v2.0
- v1.0
- Glossary
Data Check in the Sharding Scenario
sync-diff-inspector supports data check in the sharding scenario. Assume that you use the TiDB Data Migration tool to replicate data from multiple MySQL instances into TiDB, you can use sync-diff-inspector to check upstream and downstream data.
For scenarios where the number of upstream sharded tables is small and the naming rules of sharded tables do not have a pattern as shown below, you can use Datasource config to configure table-0, set corresponding rules and configure the tables that have the mapping relationship between the upstream and downstream databases. This configuration method requires setting all sharded tables.
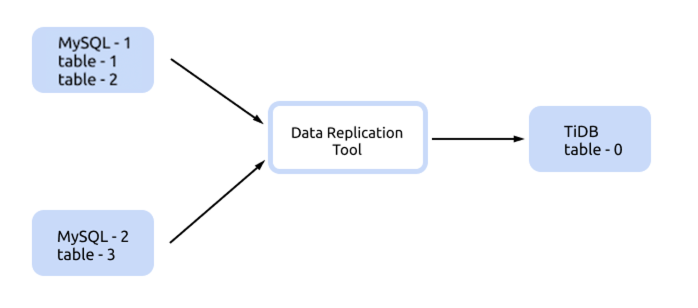
Below is a complete example of the sync-diff-inspector configuration.
# Diff Configuration.
######################### Global config #########################
# The number of goroutines created to check data. The number of connections between upstream and downstream databases are slightly greater than this value
check-thread-count = 4
# If enabled, SQL statements is exported to fix inconsistent tables
export-fix-sql = true
# Only compares the table structure instead of the data
check-struct-only = false
######################### Datasource config #########################
[data-sources.mysql1]
host = "127.0.0.1"
port = 3306
user = "root"
password = ""
route-rules = ["rule1"]
[data-sources.mysql2]
host = "127.0.0.1"
port = 3306
user = "root"
password = ""
route-rules = ["rule2"]
[data-sources.tidb0]
host = "127.0.0.1"
port = 4000
user = "root"
password = ""
########################### Routes ###########################
[routes.rule1]
schema-pattern = "test" # Matches the schema name of the data source. Supports the wildcards "*" and "?"
table-pattern = "table-[1-2]" # Matches the table name of the data source. Supports the wildcards "*" and "?"
target-schema = "test" # The name of the schema in the target database
target-table = "table-0" # The name of the target table
[routes.rule2]
schema-pattern = "test" # Matches the schema name of the data source. Supports the wildcards "*" and "?"
table-pattern = "table-3" # Matches the table name of the data source. Supports the wildcards "*" and "?"
target-schema = "test" # The name of the schema in the target database
target-table = "table-0" # The name of the target table
######################### Task config #########################
[task]
output-dir = "./output"
source-instances = ["mysql1", "mysql2"]
target-instance = "tidb0"
# The tables of downstream databases to be compared. Each table needs to contain the schema name and the table name, separated by '.'
target-check-tables = ["test.table-0"]
You can use table-rules for configuration when there are a large number of upstream sharded tables and the naming rules of all sharded tables have a pattern, as shown below:
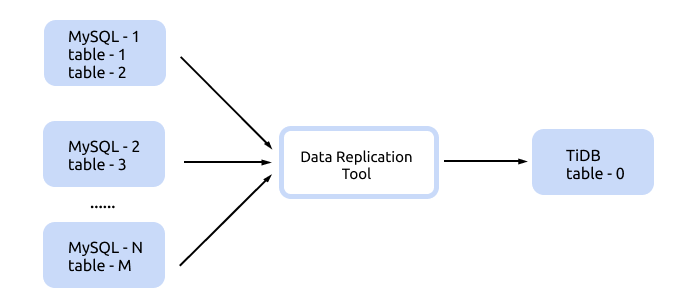
Below is a complete example of the sync-diff-inspector configuration.
# Diff Configuration.
######################### Global config #########################
# The number of goroutines created to check data. The number of connections between upstream and downstream databases are slightly greater than this value.
check-thread-count = 4
# If enabled, SQL statements is exported to fix inconsistent tables.
export-fix-sql = true
# Only compares the table structure instead of the data.
check-struct-only = false
######################### Datasource config #########################
[data-sources.mysql1]
host = "127.0.0.1"
port = 3306
user = "root"
password = ""
[data-sources.mysql2]
host = "127.0.0.1"
port = 3306
user = "root"
password = ""
[data-sources.tidb0]
host = "127.0.0.1"
port = 4000
user = "root"
password = ""
########################### Routes ###########################
[routes.rule1]
schema-pattern = "test" # Matches the schema name of the data source. Supports the wildcards "*" and "?"
table-pattern = "table-*" # Matches the table name of the data source. Supports the wildcards "*" and "?"
target-schema = "test" # The name of the schema in the target database
target-table = "table-0" # The name of the target table
######################### Task config #########################
[task]
output-dir = "./output"
source-instances = ["mysql1", "mysql2"]
target-instance = "tidb0"
# The tables of downstream databases to be compared. Each table needs to contain the schema name and the table name, separated by '.'
target-check-tables = ["test.table-0"]
Note
If test.table-0 exists in the upstream database, the downstream database also compares this table.